Introduction
Welcome to an exploration of the application of the captivating Double Field Revolving Theory in the realm of induction motors. In this article, we delve into the fascinating interplay between the theory’s revolving fields and the principles of electromagnetic induction. Prepare to unveil the secrets of how this theory enhances the efficiency and performance of induction motors.
Understanding the Double Field Revolving Theory in Induction Motors
The Double Field Revolving Theory finds compelling applications in the realm of induction motors, where the interplay between rotating magnetic fields and the principles of induction gives rise to remarkable performance enhancements. Let’s delve deeper into this exciting theory and its implications in the context of induction motors.
Double Field Revolving Theory: A Brief Overview
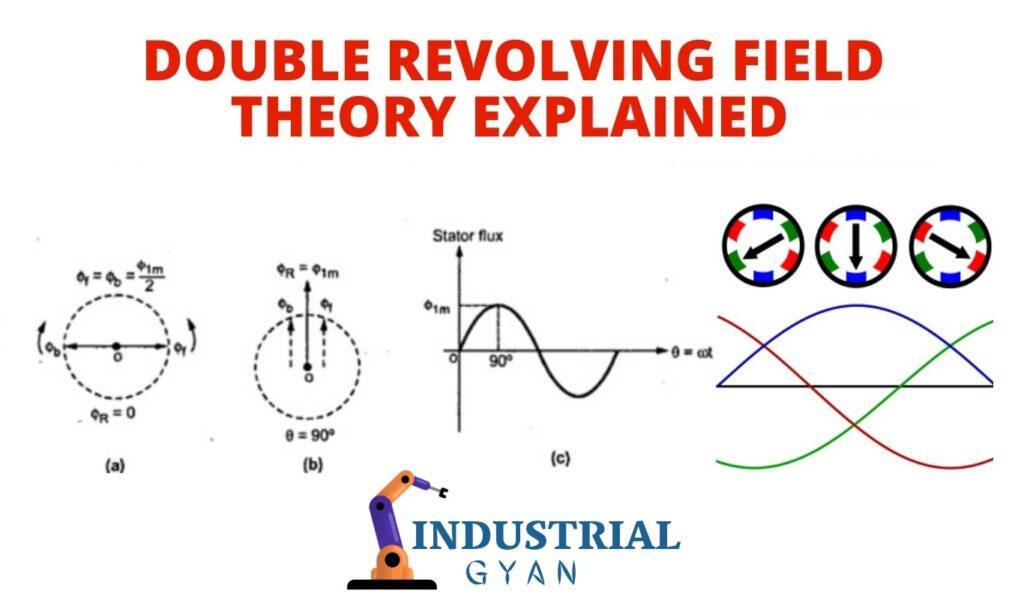
The Double Field Revolving Theory proposes that the universe operates through the interaction of two primary revolving fields: the Field of Matter and the Field of Energy. In the case of induction motors, this theory is applied to the rotating magnetic fields generated by the stator and rotor windings.
Field of Matter: Stator Winding
In an induction motor, the stator winding represents the Field of Matter. It consists of a series of coils wound around the stator core. When an alternating current (AC) is passed through these coils, a rotating magnetic field is generated, which serves as the driving force for the motor.
Sub-heading: The Dance of Magnetic Fields: Stator’s Role in Induction
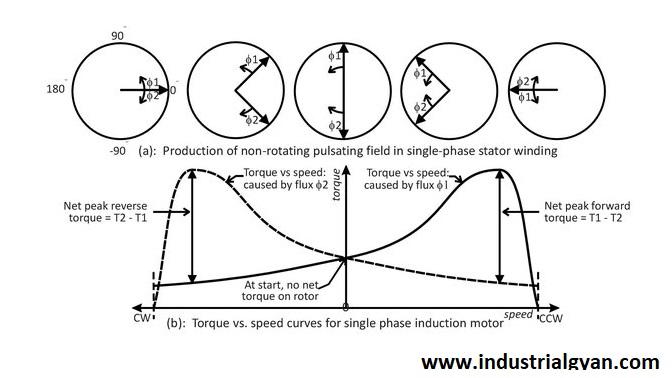
The rotating magnetic field generated by the stator winding sets the stage for the induction process in the motor. As the magnetic field revolves, it induces a voltage in the rotor winding, facilitating the flow of current and the production of torque, resulting in motor rotation.
Field of Energy: Rotor Winding
The rotor winding represents the Field of Energy in the context of induction motors. It consists of conductive bars or coils placed within the rotor core. As the stator’s magnetic field rotates. It induces a voltage in the rotor winding, which in turn generates a magnetic field.
Sub-heading: Harnessing Induction: Rotor’s Response to the Magnetic Field
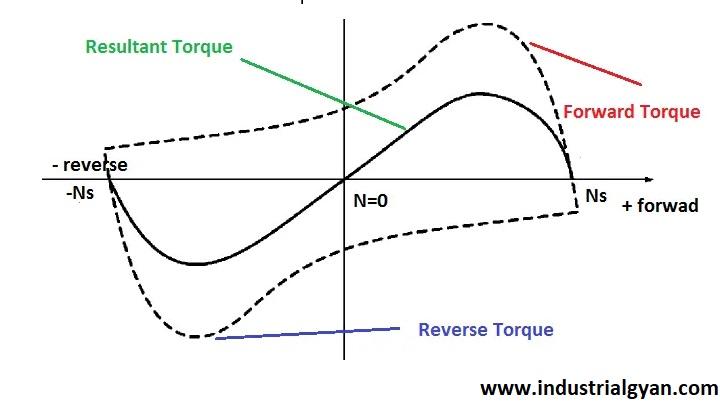
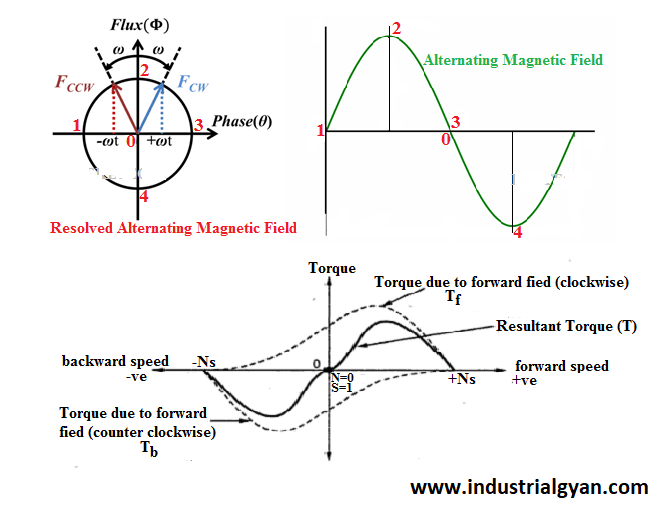
The induced magnetic field in the rotor winding interacts with the stator’s magnetic field, causing the rotor to rotate in an attempt to align itself with the rotating magnetic field.
This asynchronous rotation gives rise to the motor’s performance, providing the necessary torque and enabling various applications.
Enhancing Efficiency and Performance with the Double Field Revolving Theory
The application of the Double Fields Revolving Theory in induction motors yields significant benefits in terms of efficiency and performance. Let’s explore some of the ways in which this theory enhances the operation of induction motors.
Higher Torque Production: Optimal Power Output
The interplay between the rotating magnetic fields in the stator and rotor windings, as guided by the Double Fields Revolving Theory, leads to higher torque production. This allows induction motors to deliver optimal power output, making them ideal for a wide range of industrial and commercial applications.
Improved Energy Efficiency: Reduced Losses
By leveraging the principles of the Double Fields Revolving Theory, induction motors can achieve improved energy efficiency. The synchronized rotation of the stator and rotor magnetic fields minimizes energy losses, resulting in a more efficient conversion of electrical energy into mechanical power.
Smooth Operation: Reduced Vibrations and Noise
The Double Fields Revolving Theory promotes smoother operation in induction motors. The balanced interplay of the magnetic fields reduces vibrations and noise, ensuring a quieter and more comfortable working environment.
Robust Performance: Enhanced Reliability
Induction motors incorporating the Double Field Revolving Theory exhibit enhanced reliability. The optimized interaction between the stator and rotor fields reduces wear and tear, extending the motor’s lifespan and reducing the need for frequent maintenance.
FAQs about the Double Field Revolving Theory in Induction Motors
Here are some frequently asked questions about the application of the Double Field Revolving Theory in induction motors, along with concise answers to deepen your understanding.
- Q: How does the Double Fields Revolving Theory impact the efficiency of induction motors?
A: The theory enhances efficiency by optimizing the interaction between the stator and rotor magnetic fields, resulting in reduced energy losses and improved power conversion.
- Q: What are the advantages of using the Double Field Revolving Theory in induction motors?
A: The theory leads to higher torque production, improved energy efficiency, smoother operation, and enhanced reliability in induction motors.
- Q: Does the Double Fields Revolving Theory impact the noise level of induction motors?
A: Yes, the theory promotes smoother operation, reducing vibrations and noise in induction motors.
- Q: Are there any specific industrial or commercial applications that benefit from the Double Fields Revolving Theory in induction motors?
A: Induction motors with the Double Field Revolving Theory find applications in various industries, including manufacturing. HVAC systems, and transportation.
- Q: Is the Double Fields Revolving Theory applicable only to three-phase induction motors?
A: While the theory is commonly applied to three-phase induction motors. Its principles can be adapted to single-phase motors as well.
- Q: Are there any limitations or challenges associated with implementing the Double Fields Revolving Theory in induction motors?
Implementing the theory may require precise design considerations and control mechanisms to ensure optimal performance and synchronization of the magnetic fields.
Conclusion: Unleashing the Potential of Induction Motors
The application of the Double Field Revolvings Theory in induction motors unlocks a realm of enhanced efficiency, performance, and reliability. By harnessing the interplay between the rotating magnetic fields and the principles of electromagnetic induction, these motors become powerhouses in various industrial and commercial applications.
You can follow us on LinkedIn

I am a highly motivated and skilled individual with a passion for Electrical engineering. I have 1 year of experience in Robotics and Electrical engineering, which has allowed me to develop a strong set of skills in PLC, Painting Robots, SCADA. I am a quick learner and am always looking for new challenges and opportunities to expand my knowledge and skills. I am a team player and enjoy working with others to achieve a common goal. Successfully completed many projects for a various clients in the automobile sector.
Thank You