The electrical motor plays an important role in the modern era. Daily, Engineers design different types of electrical motor diagram for specific tasks we use various types of motors such as single-phase induction motors, stepper motors, and DC motors. These motors convert electrical energy into mechanical energy, based on Faraday’s law of electromechanical induction. .
What is an electrical motor?
It is an electrical device that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. The principle is based on the current-carrying conductor in the magnetic field experiencing a force to generate force. The resultant of the magnetic field and electromechanical flux give resultant is the direction of the electrical motor. Industries, robotics, automobiles, engineering machinery, and various other fields extensively use the electric motor.
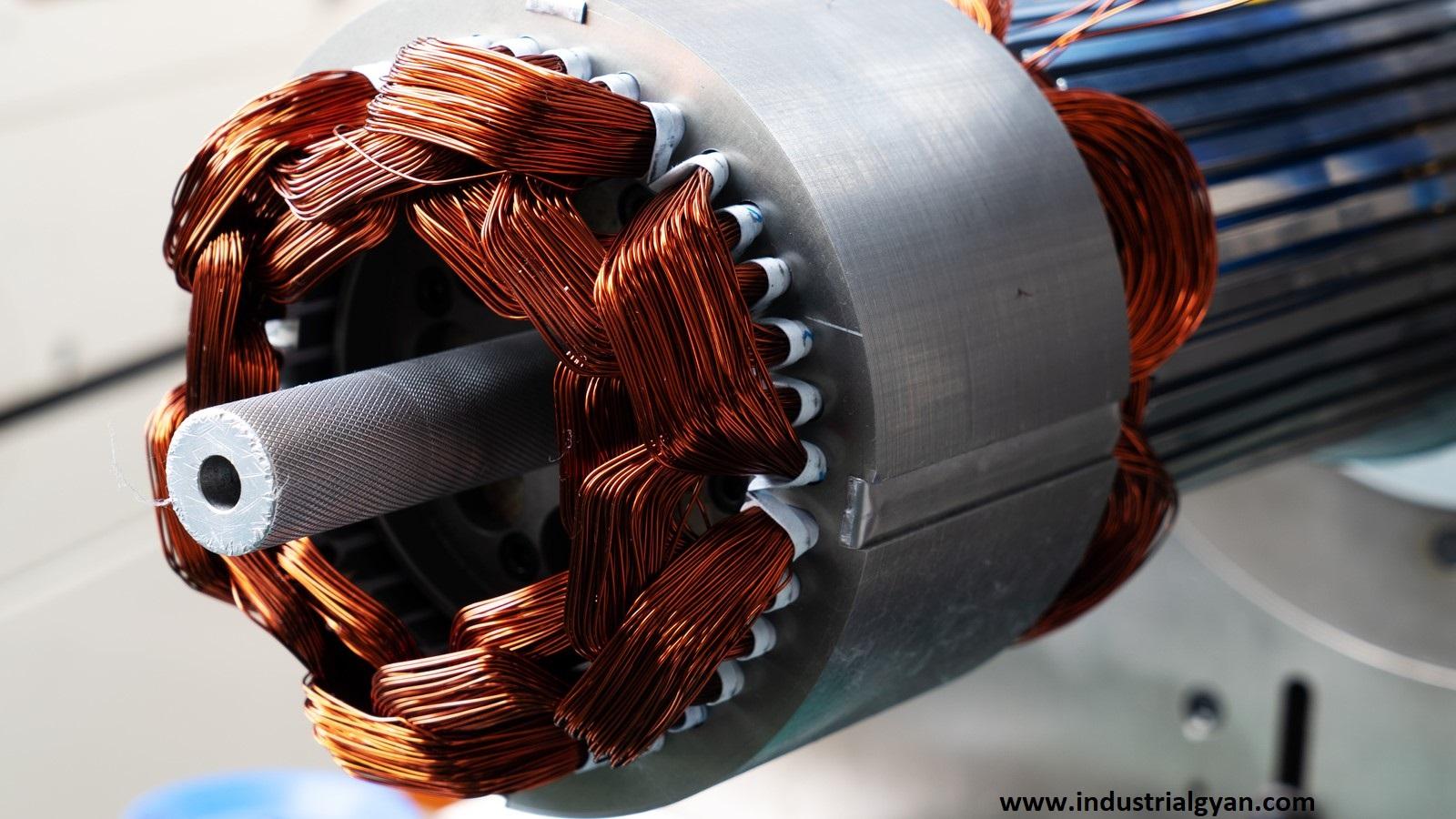
Electrical motor diagram
Construction of the electrical motor:-
The electrical motor is combined with the two parts mentioned below:-
- Stator.
- Rotor.
Stator:-
The stationary part of a motor, which connects to the alternating power supply, acts as a pole of the magnetic field. The coil of the pole connected to the AC power supply creates the magnetic field.
Rotor:-
It is the rotating part of the motor in has started the flow of the current when the stator is on an RMF (Rotating Magnetic Field). it started the flowing of the current in the rotor.
Outermost case:-
Engineers design the outer case to hold the pole in a circular form, ensuring that the winding inside is tightly packed. They construct it using cast iron.
Commutator & Brush:-
The medium of communication in a motor involves the exchange of electrical energy between the stationary and rotating parts without any mechanical intersection. One side of the stationary body is always in contact, while the other hand is connected to the rotating parts of the motor.
Working of the electrical motor:-
The stator pole is connected with the input alternating current supply. The poles started to produce the rotating magnetic field (RMF) 3-phase input power supply placed at a 120-degree angle in between them.
- A rotating magnetic field generates flux that is cut by the stator and produces the flow of the current inside the conductor.
- The flux cut by the stator current produces in the stator interferes with the magnetic field with the stator magnetic field.
- The two magnetic fields interfere with each other generating the resultant of the two magnetic fields.
- The rotor starts to experience the force in the resultant direction and increase the speed.
- In induction motor speed is always less than the rotating magnetic field speed.
Types of the electrical motor:-
- AC Motor
- DC Motor
Type of the AC motor:-
- Induction motor.
- Synchronous motor.
Type of the DC motor:-
- Self-excited motor.
- Separately excited motor.
Advantages of the electrical motor:-
- High Efficiency:-An electric motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Electric motors are highly energy-efficient, consuming less energy and resulting in lower operating costs.
- Environmental friendly:- The electrical motor is very much environmentally friendly. they produce no emission, low sound, and vibration, and also reduce the dependency on fossil fuels.
- Low maintenance:- The electrical motor required very low maintenance because of the fewer moving parts relative to the combustion engines.
- Variable speed:- The motor easily controls the speed of the electrical motor for various types of applications, to control precise speed control. In the 3 Point starter for speed control or starter
- Long life span:- The normal life of the electrical motor is comparatively very high. Also with low wear and tear risk.
Disadvantages of the electrical motor:-
- High initial cost:-The motor’s cost is comparatively high compared to a regular combustion engine, especially for a high-performance motor.
- Heating Issue:- The electrical motor generates heat during the operation. especially in case of peak performance and high load.
- Dependency on the power supply:- Highly dependent on the electrical power supply for the operation of the motor.
Alo Learn on Wikipedia

I am a highly motivated and skilled individual with a passion for Electrical engineering. I have 1 year of experience in Robotics and Electrical engineering, which has allowed me to develop a strong set of skills in PLC, Painting Robots, SCADA. I am a quick learner and am always looking for new challenges and opportunities to expand my knowledge and skills. I am a team player and enjoy working with others to achieve a common goal. Successfully completed many projects for a various clients in the automobile sector.
Thank You

