Hello guys, today we are discussing the topic of suspension type insulator, properties of the insulator, String efficiency of the insulator, advantages, and disadvantages of the insulator. Briefly covered the whole topic of suspension-type insulators including the frequently asked question (FAQ).
What is Suspension Type Insulator?
A suspension-type insulator is an electrical insulator used in high-voltage power transmission lines to suspend the conductors in air, creating a gap between the conductor and the supporting structure. The insulator prevents the flow of current from the conductor to the supporting structure and also provides mechanical support to the conductor.
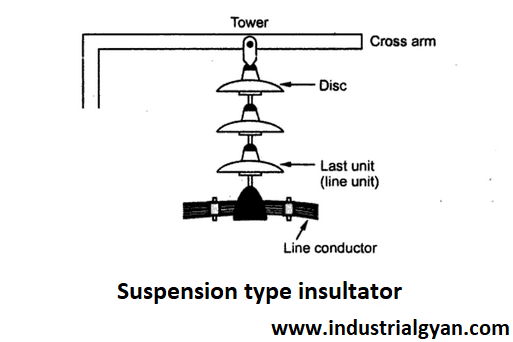
Suspension-type insulators consist of a number of insulator units connected in series by metal links or rods.
The insulator’s design ensures the uniform distribution of the electric field across its surface, thereby minimizing the risk of electrical breakdown when the voltage exceeds 33 kV. It finds common usage in power transmission lines.
Properties of the suspension-type insulator
- Electrical Insulation:- Suspension-type insulators aim to deliver high electrical insulation resistance, effectively preventing current flow from the conductor to the supporting structure.These insulators consist of materials like porcelain or glass, known for their high dielectric strength.
- Mechanical Strength:- The insulator must be able to withstand the mechanical stresses caused by the weight of the conductor and the wind loads acting on it.Suspension-type insulators possess high mechanical strength to support the conductor without breaking.Regarding resistance to weathering:- the insulator needs to withstand the impacts of UV radiation, rain, and temperature changes. Suspension-type insulators utilize weathering-resistant materials that endure prolonged exposure to the elements for many years.
- Corrosion Resistance:- The insulator must be resistant to corrosion. Due to exposure to various chemicals and pollutants in the environment, suspension-type insulators require resistance to corrosion. Therefore, they utilize materials like porcelain, glass, or composite materials that possess this property.
- Self Cleaning:- In terms of self-cleaning, suspension-type insulators are designed to automatically remove any accumulated dirt or debris on their surface through rain or other forms of precipitation.
star delta starter control diagram This ensures that the insulator remains clean and maintains its electrical properties over time.
Construction of the suspension-type insulators
- Insulator Body:-The insulator body, typically made of porcelain or glass, takes the form of a bell or a disc and provides electrical insulation between the conductor and the supporting structure.
- Metal end fittings:– connect the insulator to the conductor and the supporting structure, and they may consist of steel or other metals that resist corrosion.
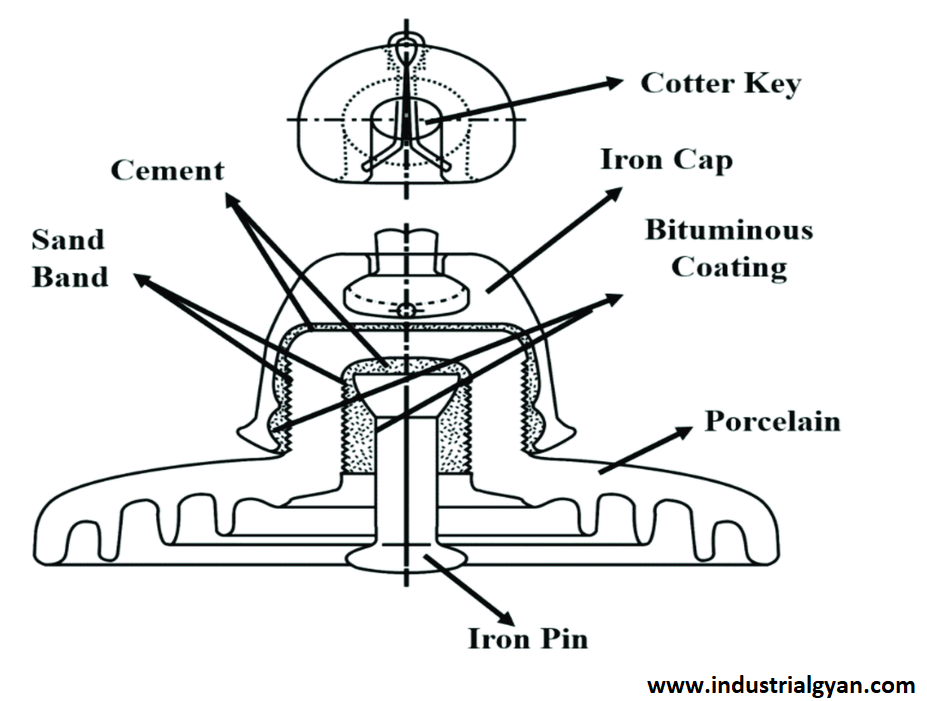
- Cement:- joins the insulator body to the metal end fittings, with the requirement that it withstand the mechanical stresses and environmental conditions encountered by the insulator.
- Assembly:- To assemble the insulator, the metal end fittings attach to the insulator body using cement. The cured insulator ensures the complete set of the cement
- Quality Control:- The completed insulator undergoes a variety of tests to ensure that it meets the required electrical and mechanical specifications. Pipe earthing diagram These tests may include high voltage tests, mechanical strength tests, and visual inspections.
String efficiency of the insulator
The string efficiency of an insulator can be calculated using the following equation:
String Efficiency = [(N-1)/(N-K)] x 100%
N = Number of insulators in the string.
K = Number of defective insulators in the string.
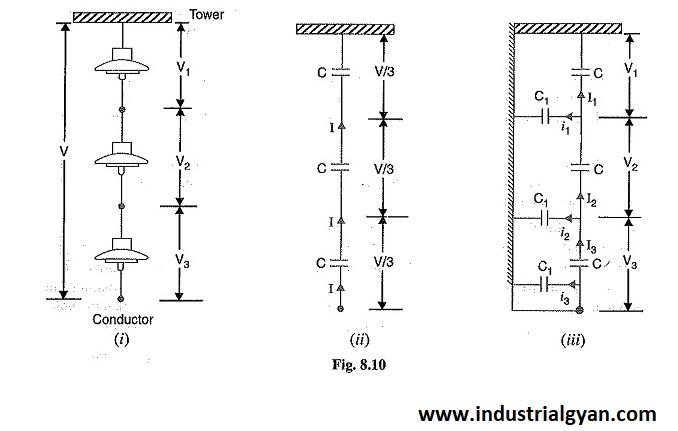
The term (n-1) in the numerator of the equation represents the voltage drop across all the insulators in the string except for the end insulator
The term (n-k) in the denominator represents the number of effective insulators in the string. Where k is the number of defective insulators.
Type of the insulator
Several types of insulators are listed below:
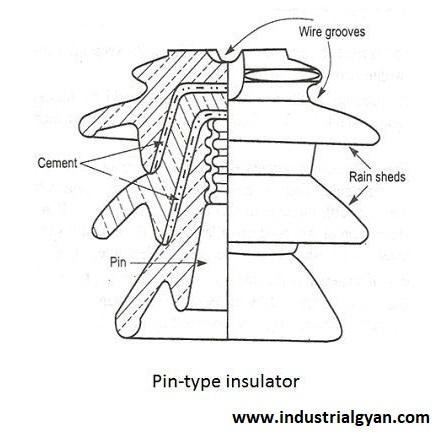
- Pin type insulator:- This insulator type finds application in low-voltage power transmission and distribution systems. It comprises a single insulator unit that mounts on a metal pin and directly attaches to the supporting structure.
- suspension type insulator:- High-voltage power transmission lines employ this insulator type. It comprises multiple insulator units connected in series using metal links or rods. The insulators hang from the supporting structure and offer electrical insulation between the conductor and the structure.
- Strain-type insulator:- This insulator type serves to mechanically support the conductor when it experiences tension or compression forces. It is designed to endure the mechanical stress resulting from these forces.
- Post-insulator:- Substations and other high-voltage applications utilize this insulator type. It consists of a single insulator unit mounted on a metal post to provide support for high-voltage equipment.
- Composite insulator: This insulator type, composed of a combination of materials like fiberglass and silicone rubber. Offers benefits in high-voltage applications. Composite insulators offer excellent electrical insulation and mechanical strength.
You can follow us on LinkedIn

I am a highly motivated and skilled individual with a passion for Electrical engineering. I have 1 year of experience in Robotics and Electrical engineering, which has allowed me to develop a strong set of skills in PLC, Painting Robots, SCADA. I am a quick learner and am always looking for new challenges and opportunities to expand my knowledge and skills. I am a team player and enjoy working with others to achieve a common goal. Successfully completed many projects for a various clients in the automobile sector.
Thank You

