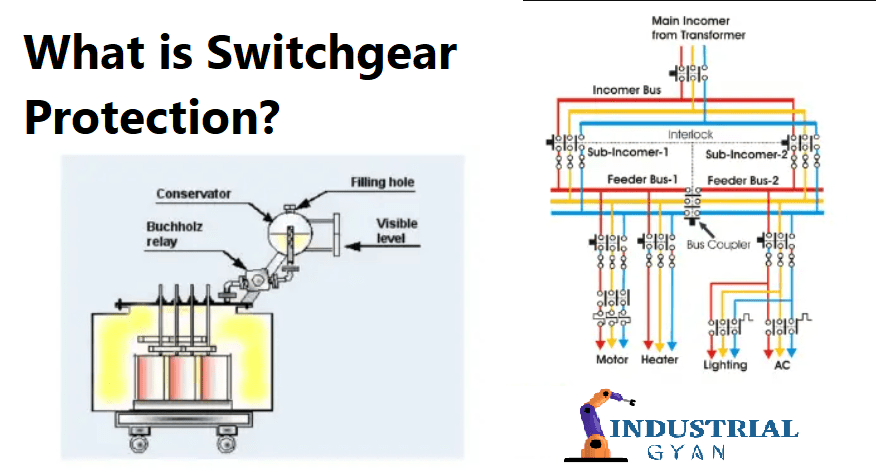
Introduction
Switchgear and protection play a crucial role in ensuring the safe and reliable operation of electrical systems. This article provides a comprehensive overview of switchgear and protection, explaining their importance, components, working principle, types, and their role in maintaining electrical safety and equipment protection. Additionally, it discusses installation and maintenance guidelines, advancements in switchgear technology, and future trends.
What is Switchgear and Protection?
Switchgear refers to a combination of electrical devices designed to control, protect, and isolate electrical equipment and circuits. It ensures the safe functioning of power systems by providing the necessary isolation, fault protection, and control mechanisms. Protection, on the other hand, involves the measures taken to detect and mitigate electrical faults, preventing damage to equipment and ensuring system reliability.
Importance of Switchgear and Protection
Switchgear and protection are vital components of any electrical system due to the following reasons:
- Electrical Safety: Switchgear and protection systems safeguard against electrical hazards, such as short circuits, overloads, and ground faults, reducing the risk of electric shocks, fires, and other accidents.
- Equipment Protection: By detecting and isolating faults, switchgear and protection mechanisms prevent damage to electrical equipment, extending its lifespan and minimizing downtime.
- System Stability: Switchgear ensures the stability of the electrical network by enabling the control and regulation of power flows, voltage levels, and frequency.
Components of Switchgear
Switchgear comprises various components that work together to control and protect electrical systems. Some essential components include:
4.1 Circuit Breakers
Circuit breakers are automatic switches that detect faults and interrupt the current flow during abnormal conditions. They provide protection against short circuits, overloads, and other electrical faults.
4.2 Fuses
Fuses are protective devices that contain a metal wire that melts when exposed to excessive current. They act as sacrificial elements, breaking the circuit and preventing damage to equipment.
4.3 Relays
Relays are devices that monitor electrical parameters and activate protective actions when predefined conditions are met. They play a critical role in fault detection and isolation.
4.4 Isolators
Isolators, also known as disconnect switches, are mechanical switches used for isolating electrical equipment from the power source. They ensure safe maintenance and repair operations by providing a visible break in the circuit.
Working Principle of Switchgear
Switchgear operates on the principle of detecting abnormal electrical conditions and interrupting the current flow to protect the system. When a fault is detected, such as an overload or short circuit, the switchgear components actuate to isolate the affected section, preventing further damage.
Types of Switchgear
Switchgear is available in various types, catering to different voltage levels and applications. The three main types are:
6.1 Low Voltage Switchgear
Low voltage switchgear is used for systems with voltage levels up to 1,000 volts. It finds applications in residential, commercial, and industrial settings, providing protection to electrical circuits and equipment.
6.2 Medium Voltage Switchgear
Medium voltage switchgear operates in the range of 1,000 to 35,000 volts and is commonly used in industrial and utility substations. It ensures the safe distribution of power within larger systems.
6.3 High Voltage Switchgear
High voltage switchgear is designed to handle voltage levels above 35,000 volts, typically used in transmission and distribution networks. It enables the reliable transmission of electricity over long distances.
Role of Switchgear and Protection
Switchgear and protection systems serve multiple roles in maintaining electrical safety, equipment protection, and system stability. Some key roles include:
7.1 Electrical Safety
Switchgear ensures the safety of personnel working with or near electrical systems by preventing electrical accidents and minimizing the risk of electric shocks and fires.
7.2 Equipment Protection
By detecting and isolating faults, switchgear protects electrical equipment from damage, preserving its operational efficiency and reducing maintenance costs.
7.3 System Stability
Switchgear devices contribute to maintaining the stability of electrical networks by controlling power flows, voltage levels, and frequency, thus preventing cascading failures and blackouts.
Installation and Maintenance
Proper installation and regular maintenance are essential for the reliable operation of switchgear and protection systems. The following guidelines should be followed:
8.1 Installation Guidelines
- Ensure proper coordination and compatibility between switchgear components.
- Follow manufacturer instructions and adhere to electrical codes and standards.
- Conduct thorough testing and commissioning to verify proper functioning.
8.2 Maintenance Practices
- Regularly inspect switchgear components for signs of wear, corrosion, or loose connections.
- Clean and lubricate mechanical parts as recommended.
- Conduct periodic testing and calibration of protective relays and circuit breakers.
Advancements in Switchgear Technology
With technological advancements, switchgear has evolved to become more intelligent, efficient, and reliable. Some notable advancements include:
- Digitalization: Integration of digital technologies for enhanced monitoring, diagnostics, and remote control capabilities.
- Smart Grid Compatibility: Switchgear is designed to support the requirements of modern smart grid systems, enabling improved energy management and grid stability.
- Innovative Insulation Materials: Adoption of advanced insulation materials with better performance and environmental sustainability.
- Arc Flash Mitigation: Development of arc-resistant switchgear designs to minimize the risks associated with arc flashes.
Future Trends
Switchgear and protection systems will experience further advancements, driven by the following trends.
- Decentralized Energy Systems: Switchgear solutions tailored for decentralized energy generation, such as solar and wind power.
- Energy Storage Integration: Integration of switchgear with energy storage systems to facilitate grid stability and demand management.
- Cybersecurity: Strengthening switchgear cybersecurity to protect against potential threats in increasingly interconnected systems.
Conclusion
Switchgear and protection systems play a critical role in ensuring the safety, reliability, and efficiency of electrical systems. By providing effective fault detection, isolation, and equipment protection, they mitigate risks and prevent potential accidents. As technology continues to advance, switchgear is becoming smarter and more capable, enabling the transition.
You can follow us on LinkedIn

I am an electrical & automation engineer with extensive experience in Design, PLC programming, SCADA development, and IoT integration. I have a strong background in the industry, focusing on the Design & Development of Hardware, Software &Industry 4.0 technologies, and the integration of intelligent manufacturing systems.
I have a deep understanding of electrical principles and am proficient in various programming languages, including Ladder Logic, Structured Text, and Python. In addition, I have experience with various PLC, SCADA & IoT technologies and a track record of successful integration projects for various clients.