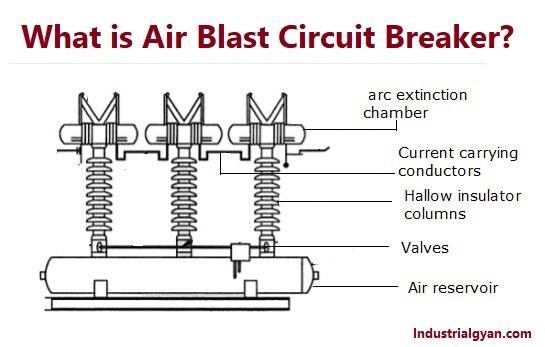
Hello guys, Today’s topic is An air blast circuit breaker (ABCB) is an electrical protection device that is commonly used in high-voltage power systems to protect against overloads and short circuits. It is designed to interrupt the flow of electric current when a fault is detected in the system, thereby protecting the equipment and ensuring the safety of personnel.
What is an air blast circuit breaker?
The basic principle behind an ABCB is the use of compressed air to extinguish the electrical arc that is generated when the contacts of the circuit breaker are opened. When a fault occurs, the circuit breaker trips and the contacts are separated, which causes a high-voltage arc to form between them.
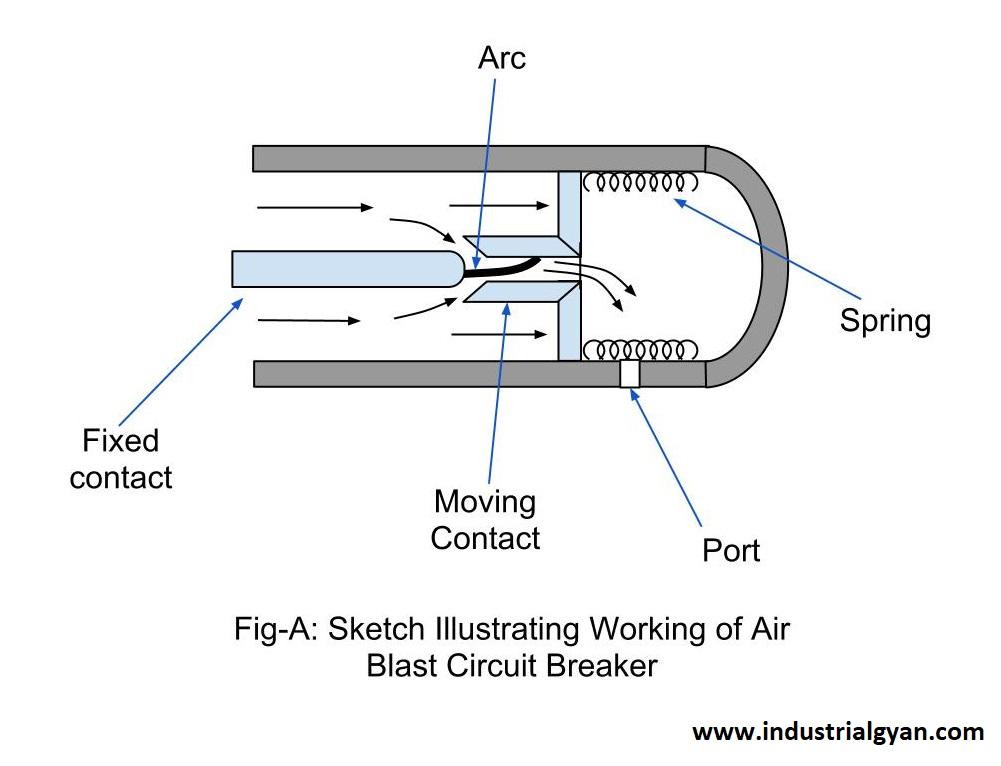
The arc is very hot and can cause damage to the equipment and create a safety hazard. In order to extinguish the arc quickly and efficiently. The ABCB releases a blast of compressed air through a nozzle that is aimed at the arc. The air cools and blows out the arc, thereby interrupting the flow of current and protecting the system.
Working of The Air Blast Circuit:-
The working of the air blast circuit can be explained in the following steps:-
- Detection of Fault:- When a fault occurs in the power system. Such as overloading or short-circuiting, The control system of the ABCB detects the fault through various sensors and switches.
- Tripping the Circuit Breaker:- Once the fault is detected, the control system triggers the circuit breaker to trip, i.e. It opens the contacts of the breaker to interrupt the flow of current.
- Formation of Arc:- As the contacts of the breaker open, a high-voltage arc is formed between them due to the ionization of the air in the gap between the contacts. This arc is very hot and can cause damage to the equipment and create a safety hazard.
- Release of Compressed Air:- To extinguish the arc, the ABCB releases a blast of compressed air through a nozzle that is aimed at the arc. The air cools and blows out the arc. Thereby interrupting the flow of current and protecting the system.
- Restoration of Contacts:- After the arc is extinguished. The contacts of the breaker are restored to their closed position, thereby restoring the flow of current through the system.
Construction of the air clast circuit breaker
The construction of the air blast circuit breaker can be explained in the following steps:-
- Interrupter Assembly:- The interrupter assembly is the main component of the ABCB and is responsible for interrupting the flow of current and extinguishing the arc. It consists of fixed and moving contacts that are separated by a small gap when the circuit is open. The moving contacts are operated by the operating mechanism of the breaker.
- Operating Mechanism:- The operating mechanism of the ABCB is responsible for opening and closing the contacts of the breaker. It can be either hydraulic or pneumatic and uses a piston or a cylinder to operate the moving contacts.
- Control System:- The control system of the ABCB includes various sensors and switches that detect faults and control the operation of the breaker. It also includes a control panel that displays. The status of the breaker and allows for manual operation.
- Compressor:- The compressor is responsible for compressing and storing. The air that is used to extinguish the arc. It is typically a reciprocating or rotary compressor that is powered by an electric motor.
- Air Tanks:- The air tanks are used to store the compressed air that is used to extinguish the arc. They are typically made of steel and are designed to withstand high pressures.
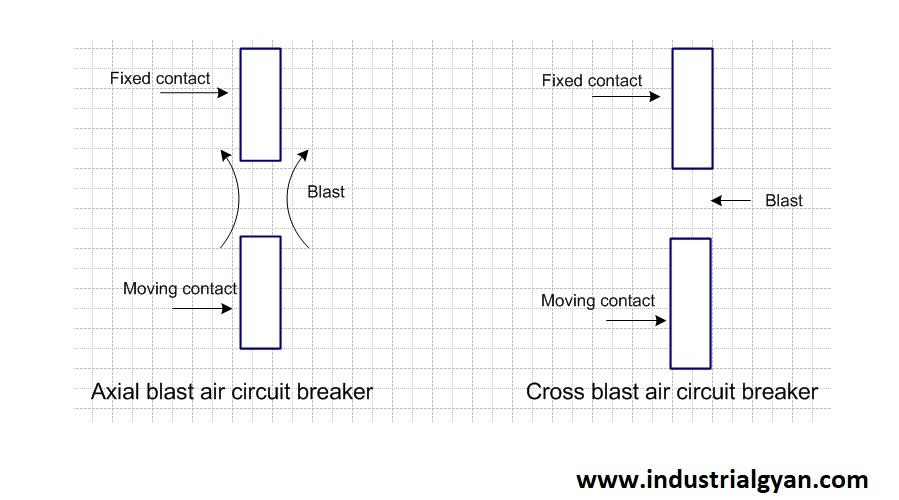
Comparison between the airblast circuit breaker and oil circuit breaker:-
Here is some comparison between the air blast circuit breaker and the oil circuit breaker
- Arc Quenching Medium:- ABCBs use compressed air as the arc quenching medium, while OCBs use oil.
- Maintenance:- ABCBs require less maintenance as compressed air is clean and does not require frequent replacement. OCBs require regular maintenance as oil needs to be filtered, checked for impurities, and replaced periodically.
- Safety:- ABCBs are relatively safer as no oil is present, reducing the risk of fires and environmental damage. OCBs are more prone to fires and environmental damage due to the presence of oil.
- Cost:- ABCBs are generally less expensive than OCBs.
- Capacity:- ABCBs are suitable for interrupting high currents and voltages up to 132 kV. OCBs are suitable for interrupting high currents and voltages up to 765 kV.
- For more information click here Industrialgyan.
Frequently asked questions:-
1)What are the advantages of an air blast circuit breaker?
Some advantages of ABCBs include their relatively low cost, suitability for interrupting high currents and voltages, smaller size and weight compared to other types of circuit breakers, and their relatively simple and reliable design.
2)What are the disadvantages of an air blast circuit breaker?
Some disadvantages of ABCBs include their need for a clean and dry compressed air supply, their sensitivity to changes in pressure and temperature, and their limited capacity for interrupting short-circuit currents.
3)What are the applications of air blast circuit breakers?
ABCBs are commonly used in high-voltage applications. Such as in power transmission and distribution systems, as well as in industrial settings where large motors and generators are used.
4) How do you maintain an air blast circuit breaker?
Maintenance of an ABCB involves regular checks on the condition of the compressed air supply, inspection and cleaning of the nozzle and other components, and checking for any signs of wear or damage.
5)What are the safety considerations when using air blast circuit breakers?
Safety considerations include the potential for high-pressure air to cause injury or damage if not handled properly, and. The need to ensure that the compressed air supply is free from moisture and contaminants that could cause malfunction or damage to the breaker.
You can follow us on LinkedIn

I am a highly motivated and skilled individual with a passion for Electrical engineering. I have 1 year of experience in Robotics and Electrical engineering, which has allowed me to develop a strong set of skills in PLC, Painting Robots, SCADA. I am a quick learner and am always looking for new challenges and opportunities to expand my knowledge and skills. I am a team player and enjoy working with others to achieve a common goal. Successfully completed many projects for a various clients in the automobile sector.
Thank You