If you are an electrical engineer or work in a related field, you have probably come across the term “insulation class” many times. Insulation class is a critical aspect of any electrical system, and understanding it is crucial for designing, testing, and maintaining electrical equipment. This article provides a comprehensive guide to insulation class, covering everything from the basics to the latest standards and regulations.
Table of Contents
- What is Insulation Class?
- The Purpose of Insulation Class
- The Types of Insulation Class
- Class 0
- Class A
- Class B
- Class F
- Class H
- Class N
- The Importance of Choosing the Right Insulation Class
- Factors Affecting Insulation Class
- Temperature
- Voltage
- Environment
- Moisture
- Chemicals
- Insulation Testing and Certification
- Insulation Class Standards and Regulations
- Conclusion
- FAQs
1. What is Insulation Class?
Insulation class refers to the thermal endurance rating of electrical insulation material. It determines the maximum temperature that the insulation can withstand without losing its electrical and mechanical properties. In other words, insulation class is a measure of the ability of the insulation to resist breakdown under high temperature and voltage.

2. The Purpose of Insulation Class
The primary purpose of the insulation class is to ensure the safety and reliability of electrical equipment. Electrical systems generate heat during operation, and if the insulation material cannot withstand high temperatures, it can break down, leading to equipment failure, fire, or even electrical shock. Insulation class helps to prevent such incidents by providing a standardized way of rating insulation materials and specifying their maximum operating temperature.
3. The Types of Insulation Class
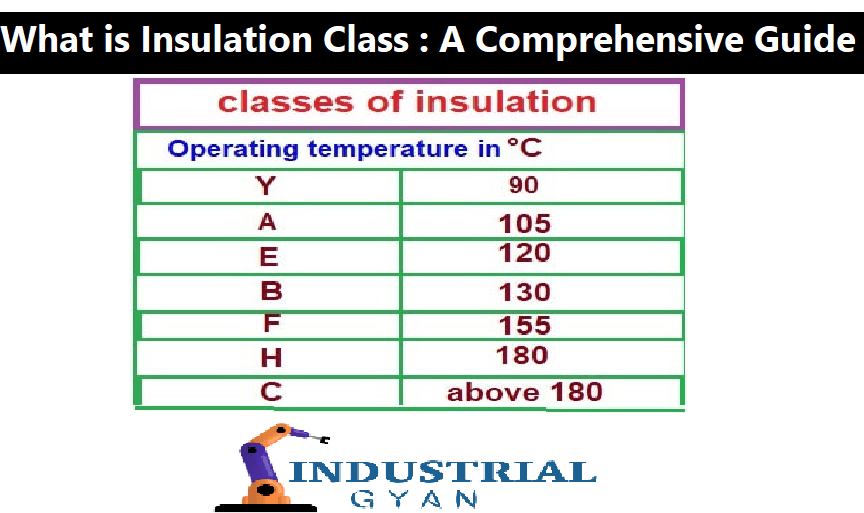
There are several types of insulation classes, each with its own maximum temperature rating. The most commonly used insulation classes are as follows:
Class 0
The Class 0 is an outdated insulation classes that is no longer used in modern electrical equipment. It has a maximum temperature rating of 100°C and was primarily used for low-voltage applications. Transformer Parts diagram
Class A
The Class A insulation has a maximum temperature rating of 105°C and is suitable for low-temperature applications, such as motors and transformers.
Class B
The Class B insulation has a maximum temperature rating of 130°C and is suitable for medium-temperature applications, such as household appliances and lighting fixtures.
Class F
The Class F insulation has a maximum temperature rating of 155°C and is suitable for high-temperature applications, such as industrial equipment and power tools.
Class H
The Class H insulation has a maximum temperature rating of 180°C and is suitable for very high-temperature applications, such as high-power transformers and generators.
Class N
The Class N insulations is a relatively new insulation classes that has a maximum temperature rating of 200°C. It is suitable for high-temperature applications, such as traction motors and wind turbines.

4. The Importance of Choosing the Right Insulation Classes
Choosing the right insulation classes is critical for ensuring the safety and reliability of electrical equipment. If the insulation material cannot withstand the operating temperature of the equipment, it can degrade, leading to insulation failure and equipment breakdown. In addition, using insulation classes that is too high for the application can result in unnecessary costs and inefficiencies. Construction of DC Machine
5. Factors Affecting Insulation Class
Several factors can affect the insulation classes of electrical equipment, including temperature, voltage, environment, moisture, and chemicals. Understanding these factors is essential for selecting the appropriate insulation classes and ensuring the long-term performance of the equipment.
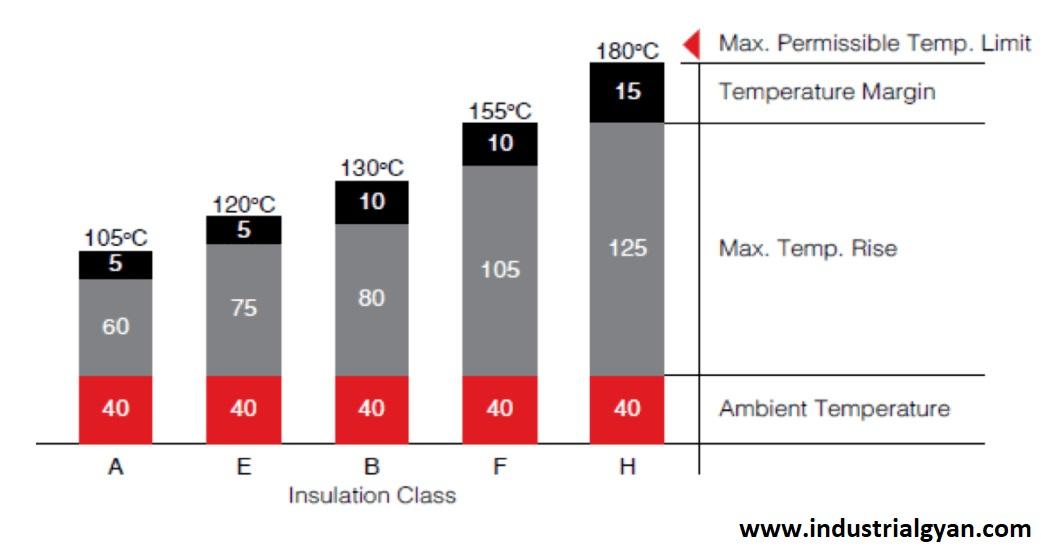
Temperature
Temperature is one of the most critical factors affecting insulation classes. The insulation material must be able to withstand the highest temperature that the equipment will generate during operation. If the temperature exceeds the maximum rating of the insulation, the material can degrade, leading to electrical breakdown, equipment failure, and fire.
Voltage
Voltage is another crucial factor affecting insulation classes. The higher the voltage, the more stress the insulation material experiences, which can cause it to degrade over time. Therefore, it is essential to choose insulation classes that can withstand the voltage requirements of the equipment.
Environment
The environment in which the equipment operates can also affect the insulation classes For example, equipment operating in a corrosive or humid environment may require a higher insulation classes to prevent degradation of the insulation material.
Moisture
Moisture is another factor that can affect the insulation classes. If the insulation material becomes wet, it can lose its dielectric properties, leading to electrical breakdown. Therefore, it is essential to select insulation classes that can withstand the moisture requirements of the equipment.
The Chemicals Affects
Chemicals present in the environment can also affect the insulation classes of electrical equipment. Chemicals can cause degradation of the insulations material, leading to electrical breakdown and equipment failure. Therefore, it is important to choose an insulation classes that can withstand exposure to the specific chemicals present in the equipment’s environment.
6. Insulation Testing and Certification
The Insulation testing and certifications are critical in ensuring that electrical equipment is safe to use. Insulation testing involves subjecting the equipment to a high voltage to determine whether the insulation material can withstand the voltage requirements of the equipment. The testing is usually conducted using specialized equipment such as a megohmmeter.
Insulations certification involves verifying that the insulation material used in the equipment meets the requirements of the relevant insulation classes. Certification is usually carried out by accredited third-party organizations that have the necessary expertise and equipment to carry out the tests.
7. Conclusion
In conclusion, insulation classes is a crucial factor in determining the safety and reliability of electrical equipment. When selecting insulation classes, it is essential to consider factors such as temperature, voltage, environment, moisture, and chemicals. It is also important to carry out insulation testing and certification to ensure that the equipment is safe to use.
8. FAQs
- What are insulation classes?
Insulations classes refer to the maximum temperature that the insulation material used in electrical equipment can withstand without degrading.
- What are the different insulation classes?
There are several insulation classes, including A, B, F, and H.
- What factors should be considered when selecting insulation classes?
The factors that should be considered when selecting insulation classes include temperature, voltage, environment, moisture, and chemicals.
- How is insulation testing carried out?
Insulation testing is usually carried out using specialized equipment such as a megohmmeter, which subjects the equipment to a high voltage to determine whether the insulations material can withstand the voltage requirements of the equipment.
- Why is insulation certification important?
Insulations certification is important in verifying that the insulations material used in the equipment meets the requirements of the relevant insulation classes, ensuring that the equipment is safe to use.
You can follow us on LinkedIn

I am a highly motivated and skilled individual with a passion for Electrical engineering. I have 1 year of experience in Robotics and Electrical engineering, which has allowed me to develop a strong set of skills in PLC, Painting Robots, SCADA. I am a quick learner and am always looking for new challenges and opportunities to expand my knowledge and skills. I am a team player and enjoy working with others to achieve a common goal. Successfully completed many projects for a various clients in the automobile sector.
Thank You