Hello guys, Today we are discussing shell-type transformers, which people most commonly use in power transmission and distribution. They named them after the way they construct the transformer core, resembling the shape of a shell. The shell-type transformer has gained widespread use and popularity.
What is a shell type of transformer?
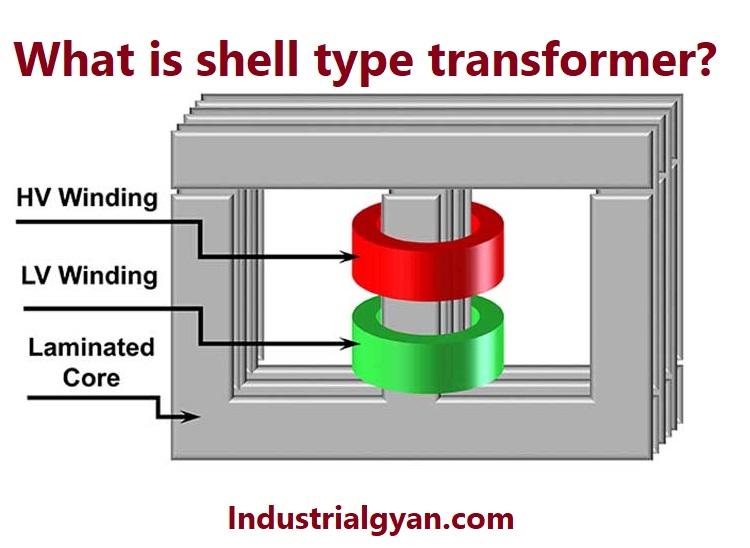
A shell-type transformer belongs to the family of core-type transformers, where the windings are wound around the core. The core consists of laminations of magnetic materials like silicon steel or iron that minimize energy loss from eddy currents.
Construction of the shell-type transformer
- Core:- The core of a shell-type transformer consists of thin laminations of magnetic materials such as silicon steel or iron. People stack the laminations together to form a closed magnetic circuit.
- Primary and Secondary Windings:- The outer layer of the transformer typically contains the primary winding, while the inner layer contains the secondary winding. The two windings are separated by an insulating layer to prevent any electrical short circuits.
- Insulation:-Insulation material typically consists of a thin layer of varnish, used to insulate the windings from each other and the core to prevent electrical short circuits.
- Tap Changer:- A tap changer is a device that changes the number of turns in the winding, typically to adjust the voltage output of the transformer to meet load requirements.
- Tank:- The transformer tank is a container that houses the core and windings. People use high-quality materials such as steel or aluminum to make the transformer capable of withstanding the high voltages and currents it experiences.
- Cooling System:- During operation, the transformer generates heat that people need to dissipate to prevent damage to the insulation and core.
.

Working of the shell type of transformer
The alternating current flows through the primary winding. It creates a magnetic field around the winding. The magnetic field passes through the core and induces a voltage in the secondary winding, which people connect to a load.
The core of the shell-type transformer consists of a series of laminated magnetic materials. They are stacked together to form a closed magnetic circuit. The laminations help to reduce the energy loss due to eddy currents, which can occur when a magnetic field passes through a conductive material.
The primary and secondary windings are placed around the core in a concentric manner. The primary winding is typically located on the outer layer of the transformer, while the secondary winding is located on the inner layer. The two windings are separated by an insulating layer. To prevent any electrical short circuits between them.
Mathematical equation related to the transformer
- Faraday’s Law:- This law states that the voltage induced in a coil is proportional. To the rate of change of the magnetic field passing through it. The equation given below is:-
E = -N dΦ/dt
- Transformer Turns Ratio:- The definition of the turns ratio of a transformer is the ratio of the number of turns in the primary winding to the number of turns in the secondary winding. We can express this relationship with the equation below::-
Np/Ns = Vp/Vs
- Transformer Impedance:- The impedance of a transformer is the ratio of the voltage to the current in the transformer.
Z = V/I
- Power in a Transformer:- The power in a transformer is equal to the product of the voltage and current in the transformer.
P = VI
Where P is the power, V is the voltage, I is the current.
Application of the shell type of transformer
. Here are some of the common applications of the shell-type transformer:
- Power Transmission:- Power transmission systems use shell-type transformers widely to step up or step down the voltage of electrical power. These transformers are designed to handle high voltage and current levels. Making it suitable for transmitting power over long distances with minimal losses.
- Industrial Applications:- People use the shell-type transformer in various industrial applications such as welding, motor control, and lighting. These applications require the transformer to handle high levels of current. Which the shell-type transformer can handle efficiently.
- Railways:- In railways, people use the shell-type transformer for traction and signaling purposes. They use the transformer to step up the voltage of the power supply to meet their needs The requirements of the traction motors used in locomotives.
- Renewable Energy:- The shell-type transformer finds widespread use in renewable energy systems such as wind and solar power plants. They use the transformer to step up the voltage of the power generated by these systems. To the level required for distribution on the grid.
- Telecommunications:- The shell-type transformer used in telecommunications systems. To isolate different parts of the system and provide power to various components.
You can follow us on LinkedIn

I am a highly motivated and skilled individual with a passion for Electrical engineering. I have 1 year of experience in Robotics and Electrical engineering, which has allowed me to develop a strong set of skills in PLC, Painting Robots, SCADA. I am a quick learner and am always looking for new challenges and opportunities to expand my knowledge and skills. I am a team player and enjoy working with others to achieve a common goal. Successfully completed many projects for a various clients in the automobile sector.
Thank You