1. Introduction
The Internet of Things (IoT) has emerged as a transformative technology that connects everyday objects and devices to the Internet, enabling data exchange and automation on a massive scale. As the IoT ecosystem continues to expand, the logical design of IoT plays a crucial role in ensuring efficient connectivity, seamless data processing, and optimal utilization of resources. This article explores the concept of IoT logical design, its components, key considerations, challenges, best practices, and future implications.
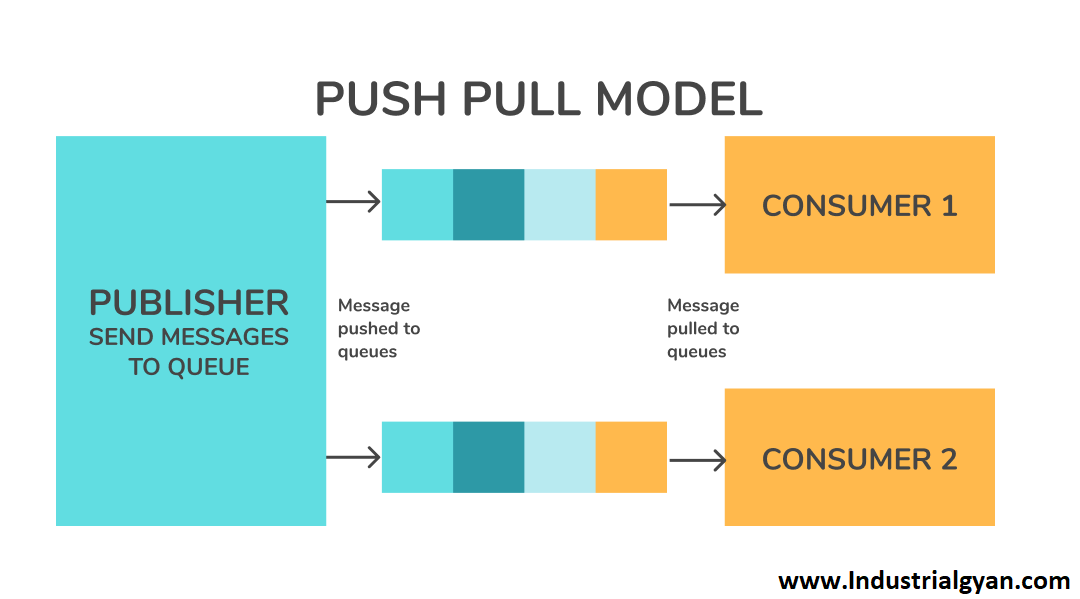
2. Understanding the Concept of IoT
IoT refers to the network of physical devices, vehicles, appliances, and other objects embedded with sensors, software, and connectivity capabilities that enable them to collect and exchange data. These devices communicate with each other and with the cloud, forming an interconnected ecosystem that facilitates real-time monitoring, control, and decision-making.
3. The Significance of Logical Design in IoT
Logical design in IoT involves structuring the network architecture and data flow to ensure efficient communication, data processing, and system performance. It encompasses the arrangement of devices, protocols, data management strategies, and application integration methods.
A well-designed logical framework optimizes data transfer, minimizes latency, and enables effective decision-making based on real-time insights. It ensures seamless interoperability, scalability, and security in the IoT ecosystem.
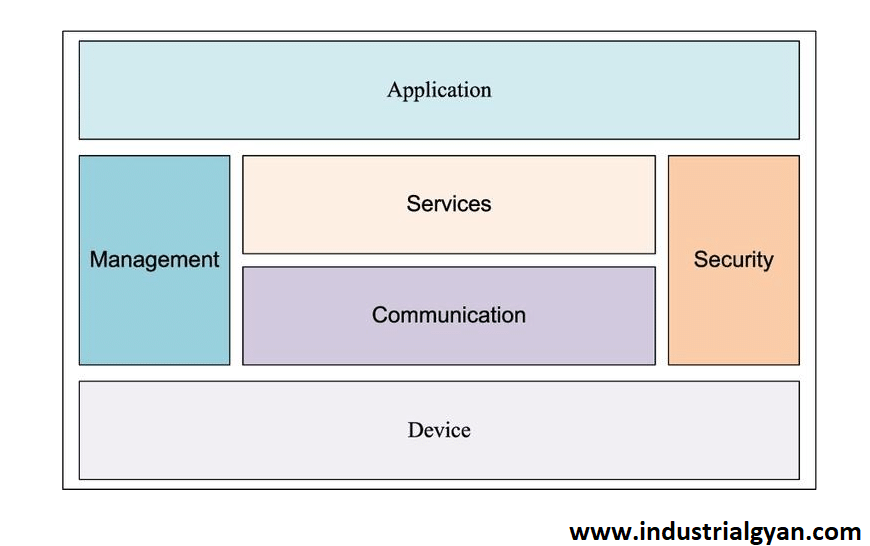
4. Components of IoT Logical Design
4.1 Device Layer
The device layer encompasses the physical IoT devices equipped with sensors, actuators, and embedded software. These devices collect data from their surroundings and transmit it to the network for further processing. The logical design of the device layer involves device selection, connectivity protocols, and firmware management.
4.2 Network Layer
The network layer deals with the connectivity infrastructure required to transmit data between IoT devices, gateways, and cloud platforms. It involves the design of communication protocols, network topologies, and quality of service (QoS) considerations. The logical design of the network layer ensures efficient data transmission, minimal latency, and reliable connectivity.
4.3 Data Layer
The data layer focuses on the management, storage, and processing of the massive amounts of data generated by IoT devices. It involves designing data models, database systems, and data analytics strategies. The logical design of the data layer ensures effective data integration, real-time analytics, and data security.
4.4 Application Layer
The application layer encompasses the software applications and services that utilize the data collected from IoT devices. It involves designing user interfaces, data visualization tools, and application programming interfaces (APIs). The logical design of the application layer ensures seamless integration with existing systems, efficient data utilization, and user-friendly experiences.
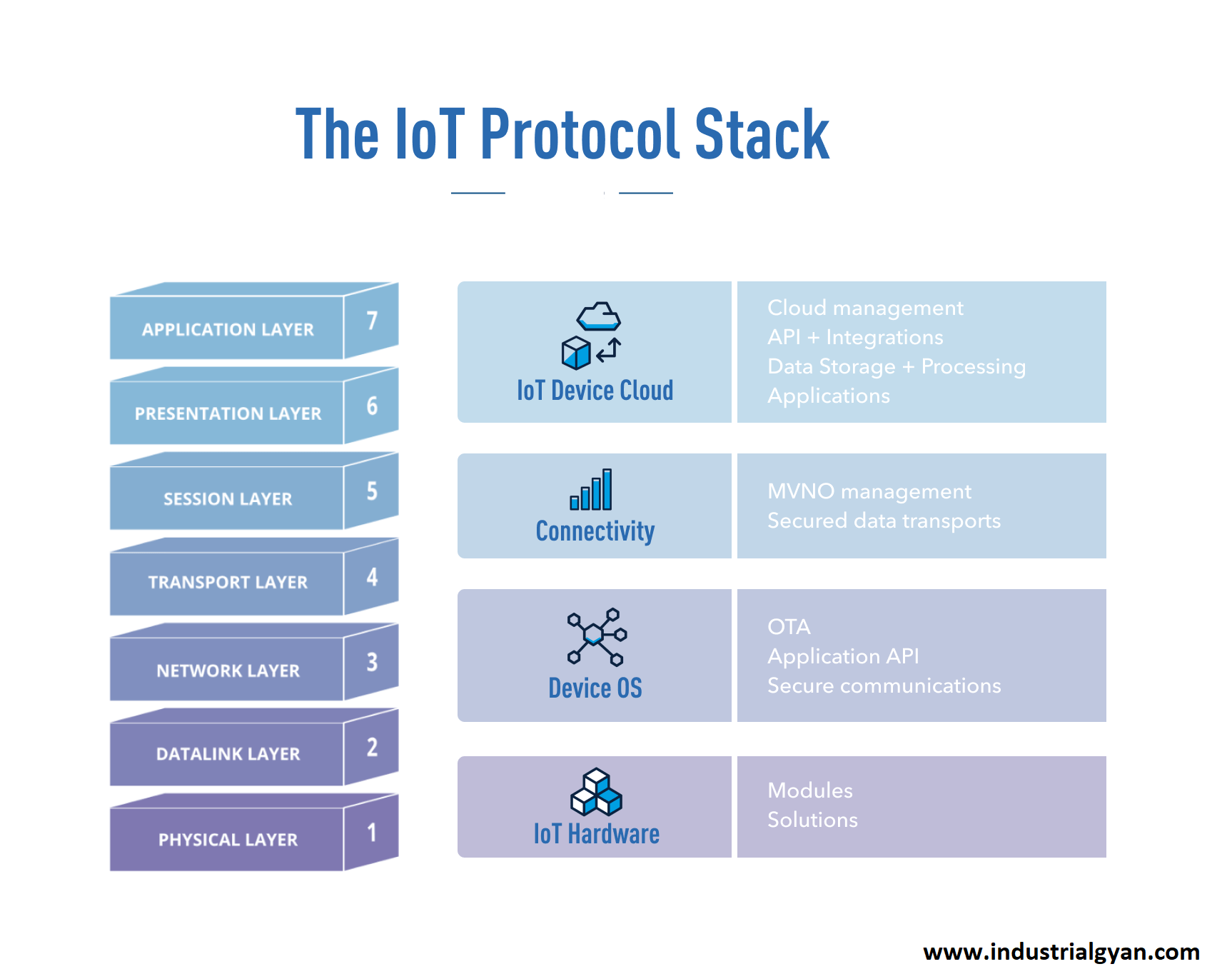
5. Key Considerations for IoT Logical Design
5.1 Scalability
IoT deployments often involve a vast number of devices and data sources. Scalability is a critical consideration in logical design, ensuring the system can handle increasing device counts, data volume, and user demands without compromising performance.
5.2 Security
Security is of paramount importance in IoT logical design. Protecting data, devices, and networks from unauthorized access, data breaches, and cyber threats is essential. Robust security measures, such as encryption, authentication, and access controls, should be integrated into the logical design.
5.3 Interoperability
Interoperability enables seamless communication and data exchange between diverse IoT devices, platforms, and applications. Standardizing protocols, data formats, and APIs ensures compatibility and enables easy integration of devices from different vendors.
5.4 Reliability
Reliability is crucial for IoT systems that require continuous data monitoring and control. Redundancy, fault tolerance, and failover mechanisms should be incorporated into the logical design to ensure uninterrupted operations and timely decision-making.
6. Challenges in IoT Logical Design
6.1 Device Heterogeneity
The diverse range of IoT devices with varying capabilities, operating systems, and communication protocols poses a challenge for logical design. Creating a flexible and scalable architecture to accommodate different devices and ensure interoperability is crucial.
6.2 Data Management
Managing and processing the massive amounts of data generated by IoT devices can be overwhelming. Efficient data storage, data cleansing, and analytics techniques need to be implemented in the logical design to extract meaningful insights from the data.
6.3 Privacy and Data Security
IoT devices often collect sensitive data, raising concerns about privacy and data security. Proper data anonymization, encryption, and access controls must be incorporated into the logical design to protect user privacy and prevent unauthorized access.
6.4 Power Consumption
IoT devices are often battery-powered or have limited power resources. Optimizing power consumption is crucial in the logical design to extend device battery life and reduce the need for frequent maintenance.
7. Best Practices for Effective IoT Logical Designs
7.1 Standardization
Standardization of protocols, data formats, and communication interfaces enables seamless integration and interoperability in the IoT ecosystem. Following industry standards and open-source frameworks simplifies the logical design process and promotes compatibility.
7.2 Modular Approach
Adopting a modular approach in logical design allows for flexibility and scalability. Proximity Effect in Transmission Lines Breaking down the IoT system into modular components simplifies maintenance, updates, and future enhancements.
7.3 Data Analytics and Processing
Leveraging advanced data analytics and processing techniques enhances the value of IoT data. Implementing real-time analytics, machine learning algorithms, and edge computing capabilities in the logical design enables rapid decision-making and actionable insights.
7.4 Cloud Integration
Integrating IoT systems with cloud platforms provides scalability, data storage, and computing capabilities. Cloud integration in the logical designs enables centralized management, data analysis, and remote access to IoT devices and applications.
8. The Future of IoT Logical Designs
The future of IoT logical design holds exciting possibilities. Advancements in technologies such as 5G, edge computing, and artificial intelligence will further enhance the efficiency and capabilities of IoT systems. The logical design will continue to evolve to meet the growing demands of diverse applications, including smart cities, industrial automation, and healthcare.
9. Conclusion
The logical design of IoT is a critical aspect of building robust and efficient IoT systems. By carefully considering device selection, network architecture, data management, and application integration, organizations can create scalable, secure, and interoperable IoT ecosystems. With proper logical designs, the potential of IoT to revolutionize industries and improve quality of life can be fully realized.
10. FAQs
Q1: How do logical designs contribute to the success of IoT projects?
The logical designs ensure efficient communication, data processing, and system performance in IoT projects. It optimizes data transfer, minimizes latency, and enables effective decision-making based on real-time insights.
Q2: What are the key challenges in IoT logical designs?
Some key challenges in IoT logical designs include device heterogeneity, data management, privacy and data security, and power consumption optimization.
Q3: What is the significance of scalability in IoT logical design?
Scalability is crucial in IoT logical design to accommodate increasing device counts, data volume, and user demands without compromising performance.
Q4: How can IoT logical design address privacy and data security concerns?
IoT logical designs can address privacy and data security concerns by incorporating measures such as data anonymization, encryption, and access controls.
Q5: What role does cloud integration play in IoT logical designs?
Cloud integration in IoT logical designs provides scalability, data storage, and computing capabilities. It enables centralized management, data analysis, and remote access to IoT devices and applications.
You can follow us on LinkedIn

I am a highly motivated and skilled individual with a passion for Electrical engineering. I have 1 year of experience in Robotics and Electrical engineering, which has allowed me to develop a strong set of skills in PLC, Painting Robots, SCADA. I am a quick learner and am always looking for new challenges and opportunities to expand my knowledge and skills. I am a team player and enjoy working with others to achieve a common goal. Successfully completed many projects for a various clients in the automobile sector.
Thank You