Introduction
If you’re in the electrical engineering or power transmission industry, you’ve likely come across the term “ACSR conductor.” In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the world of Aluminum Conductor Steel Reinforced (ACSR) conductors. We’ll explore its composition, construction, applications, advantages, and more. Whether you’re a seasoned professional or just starting your journey in this field, this article will provide you with valuable insights into ACSR conductors.
Table of Contents
- What is an ACSR Conductor?
- How is an ACSR Conductor Constructed?
- ACSR Conductor Composition
- ACSR Conductor Designations and Sizes
- ACSR Conductor Applications
- Advantages of ACSR Conductors
- Disadvantages of ACSR Conductors
- ACSR Conductor vs. Other Conductor Types
- Factors to Consider When Choosing an ACSR Conductor
- ACSR Conductor Installation
- ACSR Conductor Maintenance
- ACSR Conductor Performance in Extreme Weather Conditions
- ACSR Conductor FAQs
What is an ACSR Conductor?
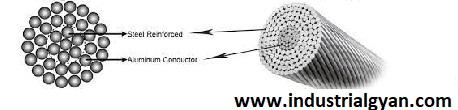
ACSR conductor, short for Aluminum Conductor Steel Reinforced, is a type of overhead power transmission conductor widely used in the utility industry. It consists of a central core made of one or more steel wires surrounded by one or more layers of aluminum wires. The steel core provides mechanical strength and improves the conductor’s overall performance.
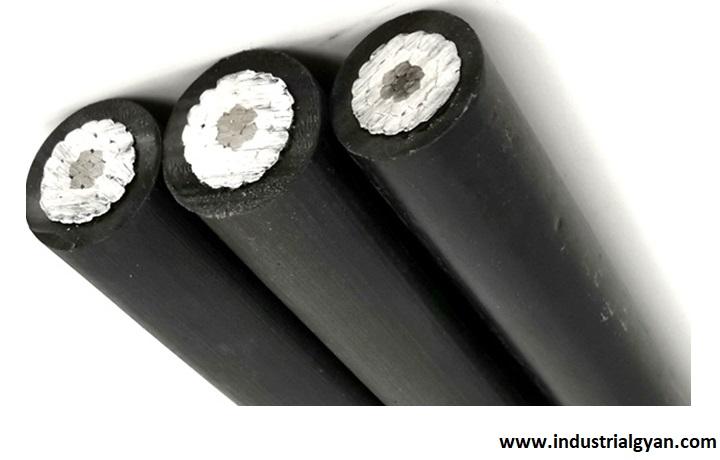

How is an ACSR Conductor Constructed?
The construction of an ACSR conductor involves combining high-strength steel and high-purity aluminum. The central strength member is formed by stranding the steel core, while the aluminum wires are stranded around it. Typically, the aluminum wires are concentrically stranded to ensure uniform current distribution and maximize efficiency.
ACSR Conductor Composition
The composition of an ACSR conductor plays a crucial role in its performance and longevity. The steel core usually consists of galvanized steel wires, which offer excellent strength and corrosion resistance. On the other hand, the aluminum wires are made of high-purity aluminum to ensure optimal conductivity. The combination of steel and aluminum in ACSR conductors creates a lightweight and robust conductor suitable for various applications.
ACSR Conductor Designations and Sizes
ACSR conductors come in different designations and sizes, each with specific characteristics and applications. The American National Standards Institute (ANSI) provides a standardized nomenclature for ACSR conductors, indicating their size and construction details. Some common ACSR conductor designations include Sparrow, Penguin, Drake, and Quail. The sizes of ACSR conductors range from 6 AWG (American Wire Gauge) to 1350 kcal (thousand circular mils).
ACSR Conductor Applications
ACSR conductors find extensive use in overhead power transmission and distribution systems. They are particularly suitable for long-distance transmission lines, where their high strength and conductivity are advantageous. ACSR conductors find common use in areas prone to severe weather conditions, as they withstand high winds, ice loading, and other environmental stresses. Moreover, ACSR conductors are employed in applications that aim to minimize electrical interference and power losses.
Advantages of ACSR Conductors
ACSR conductors offer several advantages that make them a popular choice in the industry:
- High Strength: The steel core of ACSR conductors provides excellent mechanical strength, allowing them to withstand the tension and stresses encountered in overhead power transmission.
- Optimal Conductivity: The aluminum wires in ACSR conductors offer high electrical conductivity, ensuring efficient power transmission.
- Lightweight: Despite their strength, ACSR conductors are relatively lightweight compared to all-steel conductors, making them easier to handle and install.
- Resistance to Corrosion: The galvanized steel core of ACSR conductors provides corrosion resistance, increasing their longevity and reducing maintenance requirements.
- Excellent Performance in Extreme Weather: ACSR conductors have proven their reliability in extreme weather conditions, such as high winds, ice, and snow, making them suitable for various climates and terrains.
- Cost-Effective: ACSR conductors offer a cost-effective solution for power transmission, thanks to their optimal balance between strength and conductivity.
Disadvantages of ACSR Conductors
While ACSR conductors have numerous advantages, they also have some limitations:
- Susceptibility to Galvanic Corrosion: The dissimilar metals in ACSR conductors (steel and aluminum) can lead to galvanic corrosion under certain conditions. Proper design and maintenance practices can help mitigate this issue.
- Higher Thermal Expansion: ACSR conductors have a higher coefficient of thermal expansion compared to all-aluminum conductors. This characteristic needs to be considered during installation and expansion joint design.
ACSR Conductor vs. Other Conductor Types
When considering ACSR conductors, it’s essential to understand how they compare to other conductor types commonly used in the industry. Let’s briefly explore the differences:
- ACSR vs. All-Aluminum Conductor (AAC): ACSR conductors offer higher strength and mechanical resilience compared to AAC conductors. AAC conductors are typically used in low-stress applications and areas with low ice and wind loading.
- ACSR vs. All-Aluminum Alloy Conductor (AAAC): AAAC conductors provide better corrosion resistance and higher conductivity compared to ACSR conductors. However, ACSR conductors excel in mechanical strength and are more cost-effective.
- ACSR vs. Aluminum-Clad Steel Reinforced (ACSR/AW): ACSR/AW conductors combine the strength of steel and the corrosion resistance of aluminum, offering enhanced durability and longevity. internal gear pump They are commonly used in coastal areas with high salt exposure.
Factors to Consider When Choosing an ACSR Conductor
When selecting an ACSR conductor for a specific application, several factors should be considered:
- Operating Voltage: The voltage requirements of the power transmission system play a crucial role in determining the suitable ACSR conductor size.
- Span Length: The distance between transmission towers or poles affects the tension and sag in the conductor, which should be within acceptable limits.
- Environmental Conditions: Consider the local weather conditions, such as wind speed, ice loading, and temperature range, to ensure the selected ACSR conductor can withstand these factors.
- Current Carrying Capacity: Determine the maximum current the conductor needs to carry without exceeding its thermal limits.
- Longevity and Maintenance: Evaluate the expected lifespan of the conductor and the maintenance requirements associated with its use.
- Cost Considerations: Balance the performance requirements with the project budget to find the most cost-effective solution.
ACSR Conductor Installation
Proper installation is vital to ensure the optimal performance and longevity of ACSR conductors. Here are some key considerations during installation:
- Handling and Storage: Handle ACSR conductors with care to avoid damage to the aluminum strands. Store them in a dry, well-ventilated area, and protect them from exposure to moisture and corrosive substances.
- Conductor Sag: Ensure the appropriate sag is maintained between transmission towers or poles to accommodate thermal expansion and contraction. Sagging too low or too high can affect the conductor’s performance and integrity.
- Stringing and Tensioning: Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for stringing and tensioning the ACSR conductors. Improper tension can lead to excessive sag or stress on the conductor.
- Supporting Hardware: Use suitable hardware, such as suspension clamps and spacers, to support and protect the ACSR conductors. Proper hardware selection prevents damage and ensures uniform load distribution.
- Grounding: Implement effective grounding techniques to protect personnel and equipment from electrical faults and lightning strikes.

ACSR Conductor Maintenance
Regular maintenance is essential to maximize the lifespan and performance of ACSR conductors. Here are some maintenance practices to consider:
- Visual Inspections: Regularly inspect ACSR conductors for signs of wear, corrosion, or damage. Look for broken strands, loose hardware, and any signs of structural degradation.
- Cleaning: Clean the ACSR conductors to remove dirt, debris, and contaminants that can affect their performance. Use appropriate cleaning agents and methods recommended by the manufacturer.
- Corrosion Prevention: Implement corrosion prevention measures, such as applying suitable coatings or inhibitors, to protect the steel core from rust and corrosion.
- Vegetation Management: Monitor the surrounding vegetation and ensure it does not interfere with the ACSR conductors. Trim trees and remove any vegetation that could cause mechanical stress or electrical faults.
- Thermal Monitoring: Implement thermal monitoring techniques to detect any abnormal temperature rises in the ACSR conductors. Unusual heating can indicate potential issues, such as increased resistance or current overload.
ACSR Conductors Performance in Extreme Weather Conditions
ACSR conductors have proven their reliability in extreme weather conditions. Let’s explore their performance in different scenarios:
- High Winds: ACSR conductors are designed to withstand high wind speeds. moving iron instrument The combination of steel and aluminum provides the necessary strength and flexibility to resist the forces generated by strong winds.
- Ice Loading: ACSR conductors exhibit good resistance to ice loading. The steel core provides the necessary strength to support the weight of ice while maintaining the integrity of the conductor.
- Severe Storms: ACSR conductors have a track record of performing well during severe storms. Their robust construction and ability to withstand mechanical stresses make them suitable for areas prone to hurricanes, typhoons, and other intense weather events.
- Temperature Extremes: ACSR conductors can withstand a wide range of temperature fluctuations, from extreme cold to high heat. The thermal expansion properties of the conductor are carefully considered during design to ensure optimal performance in various climates.
ACSR Conductor FAQs
- Q: What does ACSR stand for?
- A: ACSR stands for Aluminum Conductor Steel Reinforced.
- Q: What is the purpose of the steel core in an ACSR conductor?
- A: The steel core provides mechanical strength and enhances the overall performance of the conductor.
- Q: Where are ACSR conductors commonly used?
- A: ACSR conductors are extensively used in overhead power transmission and distribution systems, especially for long-distance transmission lines and areas with challenging weather conditions.
- Q: How do ACSR conductors compare to other conductor types?
- A: ACSR conductors offer a balance of strength, conductivity, and cost-effectiveness. They are often preferred for their mechanical resilience and high tensile strength.
- Q: Are ACSR conductors prone to corrosion?
- A: ACSR conductors can experience galvanic corrosion due to the dissimilar metals (steel and aluminum) present. However, proper design and maintenance practices can mitigate this issue.
- Q: Can ACSR conductors withstand extreme weather conditions?
- A: Yes, ACSR conductors have demonstrated their ability to perform well in high winds, ice loading, and severe storms. Their robust construction and materials make them suitable for various climates and terrains.
Conclusion
ACSR conductors, with their unique combination of aluminum and steel, are widely utilized in the power transmission industry. Their mechanical strength, conductivity, and performance in extreme weather conditions make them an excellent choice for overhead transmission lines. By understanding the construction, applications, advantages, and maintenance requirements of ACSR conductors, professionals in the electrical engineering field can make informed decisions regarding their implementation. Remember to consider factors such as operating voltage, environmental conditions, and current carrying capacity when choosing ACSR conductors. With proper installation, regular maintenance, and adherence to industry standards, ACSR conductors can provide reliable and efficient power transmission for years to come.
You can follow us on LinkedIn

I am a highly motivated and skilled individual with a passion for Electrical engineering. I have 1 year of experience in Robotics and Electrical engineering, which has allowed me to develop a strong set of skills in PLC, Painting Robots, SCADA. I am a quick learner and am always looking for new challenges and opportunities to expand my knowledge and skills. I am a team player and enjoy working with others to achieve a common goal. Successfully completed many projects for a various clients in the automobile sector.
Thank You
