Introduction
Have you ever wondered how electrical engineers measure current in a circuit? One remarkable device that plays a crucial role in this process is the Moving Iron Instrument. In this article, we will explore the fascinating world of moving iron instruments, their working principle, types, applications, and advantages. Whether you’re a student studying electrical engineering or simply curious about the inner workings of these instruments, this article will provide you with a comprehensive understanding of this incredible technology.
Table of Contents
- What is a Moving Iron Instrument? 1.1 Components of a Moving Iron Instrument 1.2 Working Principle of a Moving Iron Instrument
- Types of Moving Iron Instruments 2.1 Attraction Type Moving Iron Instrument 2.2 Repulsion Type Moving Iron Instrument
- Applications of Moving Iron Instruments 3.1 Electrical Power Measurement 3.2 Circuit Testing and Troubleshooting 3.3 Industrial Control Systems
- Advantages of Moving Iron Instruments 4.1 Wide Measurement Range 4.2 Robustness and Durability 4.3 Suitable for Both AC and DC Circuits
- Frequently Asked Questions 5.1 How accurate are moving iron instruments? 5.2 Can moving iron instruments be used for high-frequency measurements? 5.3 Are moving iron instruments suitable for measuring small currents? 5.4 Can moving iron instruments withstand high voltage? 5.5 What are the limitations of moving iron instruments? 5.6 Are moving iron instruments still widely used today?
- Conclusion
1. What is a Moving Iron Instrument?
The moving iron instrument, widely used in electrical engineering, is a versatile device for measuring electrical current in a circuit. It indicates the magnitude of current flowing through it by employing the principle of magnetic attraction or repulsion between a movable iron piece and fixed iron coils. These instruments are renowned for their accuracy, reliability, and capability to measure both AC and DC currents.
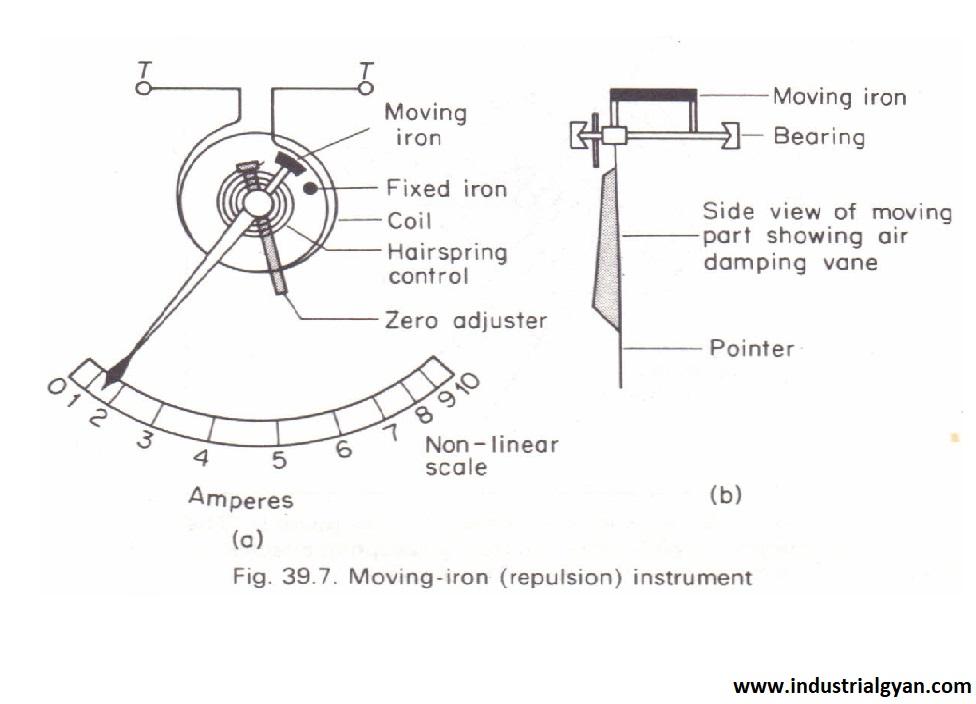
1.1 Components of a Moving Iron Instrument
A typical moving iron instrument consists of the following components:
- Movable Iron Piece: This piece is attracted or repelled by the magnetic field generated by the current in the circuit, causing it to move.
- Fixed Iron Coils: These coils produce the magnetic field that interacts with the movable iron piece.
- Hair Spring: The hair spring provides the necessary restoring force to bring the movable iron piece back to its original position when the current changes.
- Pointer: The pointer is attached to the movable iron piece and indicates the current value on a calibrated scale.
1.2 Working Principle of a Moving Iron Instrument
The working principle of a moving iron instrument is based on the fundamental law of electromagnetism – magnetic attraction and repulsion. When current flows through the fixed iron coils, it generates a magnetic field. This magnetic field interacts with the movable iron piece, resulting in the attraction or repulsion between them. The magnitude of this force depends on the current passing through the coils, allowing the instrument to measure current.
2. Types of Moving Iron Instruments
Moving iron instruments are primarily categorized into two types:
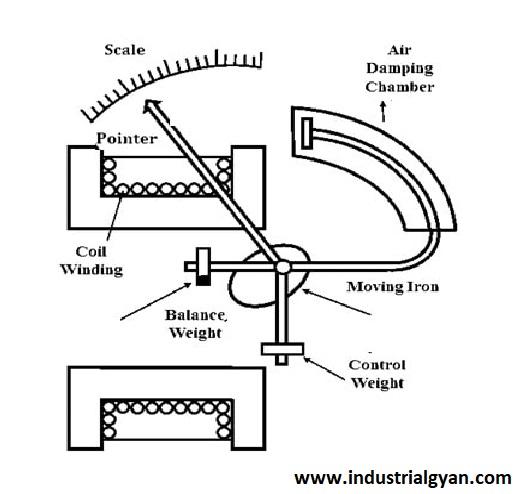
2.1 Attraction Type Moving Iron Instrument
In the attraction-type moving iron instrument, the current flowing through the fixed iron coils attracts the movable iron piece towards them. The degree of attraction is directly proportional to the current magnitude. This instrument is commonly used for measuring AC currents.
2.2 Repulsion Type Moving Iron Instrument
On the contrary, the repulsion-type moving iron instrument operates based on the principle of repulsion between the movable and fixed iron pieces. When current flows through the coils, it generates a repulsive force, pushing the movable iron piece away from the fixed coils. switched reluctance motor This instrument is typically used for measuring DC currents.
3. Applications of Moving Iron Instruments
Moving iron instruments find a wide range of applications in electrical engineering and various industries. Let’s explore a few of their key applications:
3.1 Electrical Power Measurement
One of the primary applications of moving iron instruments is electrical power measurement. These instruments can accurately measure the current flowing through power lines, helping to determine the power consumption of electrical appliances and systems. They are commonly used in residential, commercial, and industrial settings.
3.2 Circuit Testing and Troubleshooting
Moving iron instruments are invaluable tools for circuit testing and troubleshooting. By measuring the current in different parts of a circuit, engineers can identify faulty components, locate short circuits, and ensure the proper functioning of electrical systems. They are essential for maintaining the safety and reliability of electrical installations.
3.3 Industrial Control Systems
Industrial control systems widely employ moving iron instruments to monitor and regulate electrical parameters. They work in conjunction with control panels to measure current in motors, generators, transformers, and other industrial machinery. These instruments ensure that the systems operate within the desired parameters, preventing equipment damage, and enhancing overall efficiency.

4. Advantages of Moving Iron Instruments
Moving iron instruments offer several advantages that make them popular among electrical engineers and technicians. Let’s explore some of their key benefits:
4.1 Wide Measurement Range
Moving iron instruments are capable of measuring a wide range of currents, making them suitable for various applications. Whether you need to measure small currents or high currents, these instruments provide accurate readings across the entire spectrum.
4.2 Robustness and Durability
These instruments are built to withstand harsh operating conditions. With robust construction and durable materials, they can withstand mechanical shocks, vibrations, and temperature variations, ensuring reliable performance even in demanding environments.
4.3 Suitable for Both AC and DC Circuits
Unlike some other types of instruments that are limited to either AC or DC measurements, moving iron instruments offer versatility and can accurately measure both AC and DC currents. This flexibility makes them highly useful in a wide range of electrical systems.
5. Frequently Asked Questions
5.1 How accurate are moving iron instruments?
Moving iron instruments are known for their accuracy, providing reliable current measurements. The accuracy can vary depending on the instrument’s design and quality, but high-quality moving iron instruments can achieve accuracy levels of around 1-2%.
5.2 Are moving iron instruments suitable for high-frequency measurements?
Moving iron instruments are primarily designed for measuring power frequency currents, typically up to 50-60 Hz. For high-frequency measurements, specialized instruments such as digital multimeters or oscilloscopes are more suitable.
5.3 Are moving iron instruments suitable for measuring small currents?
Moving iron instruments can measure a wide range of currents, including small currents. However, for highly accurate measurements of small currents, instruments specifically designed for low-current measurements, such as current clamps, are preferred.
5.4 Can moving iron instruments withstand high voltage?
Primarily, moving iron instruments measure current rather than voltage. internal gear pump They can handle voltage drops across the instrument but usually have a voltage rating limited to a few hundred volts. To measure high voltage, it is advisable to use voltage-specific instruments.
5.5 What are the limitations of moving iron instruments?
Moving iron instruments, while versatile and reliable, do have some limitations. They may have a non-linear scale, which requires careful calibration. Additionally, they have a finite time response and may not accurately measure rapidly changing currents.
6. Conclusion
A moving iron instrument is an indispensable tool in electrical engineering, offering accurate current measurements and versatility. With their robust construction, wide measurement range, and ability to handle both AC and DC currents, these instruments have found applications in power measurement, circuit testing, and industrial control systems. Despite advancements in digital instrumentation, moving iron instruments remain a reliable choice for engineers and technicians seeking accurate current measurements. So, the next time you encounter a circuit, remember the remarkable moving iron instrument that enables us to understand and control the flow of electricity.
You can follow us on LinkedIn

I am a highly motivated and skilled individual with a passion for Electrical engineering. I have 1 year of experience in Robotics and Electrical engineering, which has allowed me to develop a strong set of skills in PLC, Painting Robots, SCADA. I am a quick learner and am always looking for new challenges and opportunities to expand my knowledge and skills. I am a team player and enjoy working with others to achieve a common goal. Successfully completed many projects for a various clients in the automobile sector.
Thank You
